By A Mystery Man Writer

Elements of A Patient Assessment SCENE SIZE-UP INITIAL ASSESSMENT FOCUSED HISTORY & PHYSICAL EXAM FOCUSED HISTORY & PHYSICAL EXAM DETAILED PHYSICAL EXAM MEDICALPATIENTTRAUMAPATIENT DETAILED PHYSICAL EXAM ON-GOING ASSESSMENT
Patient Assessment EMT/Paramedic Refresher Training.
Elements of A Patient Assessment Scene Size UpScene Size Up Initial AssessmentInitial Assessment Vitals Signs and Patient HistoryVitals Signs and Patient History Focused History and Detailed Exam Focused History and Detailed Exam Trauma Patient AssessmentTrauma Patient Assessment Medical Patient AssessmentMedical Patient Assessment Ongoing ExamOngoing Exam
Elements of A Patient Assessment SCENE SIZE-UP INITIAL ASSESSMENT FOCUSED HISTORY & PHYSICAL EXAM FOCUSED HISTORY & PHYSICAL EXAM DETAILED PHYSICAL EXAM MEDICALPATIENTTRAUMAPATIENT DETAILED PHYSICAL EXAM ON-GOING ASSESSMENT
What do we know about this scene
Checking Scene SafetyChecking Scene Safety Taking Body Substance Isolation (BSI) precautionsTaking Body Substance Isolation (BSI) precautions Noting the Mechanism of Injury or Nature of IllnessNoting the Mechanism of Injury or Nature of Illness Determining the # of patientsDetermining the # of patients Deciding if additional resources are needed.Deciding if additional resources are needed. YOU should continue to Size-up your scene throughout the call!.
Scene Size Up Begins with receipt of callBegins with receipt of call LocationLocation IncidentIncident Injured/InjuriesInjured/Injuries
Listen for other approaching Emergency Units from other directions.Listen for other approaching Emergency Units from other directions. Look for down wires, smoke, or other hazards.Look for down wires, smoke, or other hazards. Observe the traffic flow.Observe the traffic flow. Look for victims on or near the roadway.Look for victims on or near the roadway. Be alert for onlookers.Be alert for onlookers. Watch for signals from police officers or other emergency personnel.Watch for signals from police officers or other emergency personnel. Sniff for odors.Sniff for odors. The Scene Size-up begins before the ambulance ever comes to a STOP!.
A Danger Zone exist around the wreckage of every vehicle collision, within which special precautions must be taken.A Danger Zone exist around the wreckage of every vehicle collision, within which special precautions must be taken. No apparent hazards – the Danger Zone should be extended at least 50ft in all directions.No apparent hazards – the Danger Zone should be extended at least 50ft in all directions. If fuel has been spilled or a vehicle is on fire – the Danger Zone should extend a minimum of 100 ft in all directions. Park Upwind. Also if fuel has spilled, park uphill if possible.If fuel has been spilled or a vehicle is on fire – the Danger Zone should extend a minimum of 100 ft in all directions. Park Upwind. Also if fuel has spilled, park uphill if possible. If wires are down – consider the danger zone the area in which people or vehicles might be contacted by the wires if they pivoted around their attachments.If wires are down – consider the danger zone the area in which people or vehicles might be contacted by the wires if they pivoted around their attachments. When a hazardous material is involved – check the Emergency Response Guidebook.When a hazardous material is involved – check the Emergency Response Guidebook. An Ambulance should never be parked inside the DANGER ZONE!.
Return only when the scene is secured by law enforcement..
Scene Size Up Once your scene survey is complete, determine the nature of the call by identifying the mechanism of injury or the nature of illness.
certain injuries are considered common to a given situation.certain injuries are considered common to a given situation. even though you can’t determine the exact injury a patient may have sustained, knowing the mechanism of injury may allow you to predict injury patternseven though you can’t determine the exact injury a patient may have sustained, knowing the mechanism of injury may allow you to predict injury patterns.
There are actually three collisions involved in each motor vehicle crash.There are actually three collisions involved in each motor vehicle crash. 1-The force of the vehicle as it strikes an object.1-The force of the vehicle as it strikes an object. 2-The force of the patient’s body as it strikes the vehicles interior2-The force of the patient’s body as it strikes the vehicles interior 3-The force of the patient’s organs as they strike surfaces within the body.3-The force of the patient’s organs as they strike surfaces within the body. Remember The Law of Inertia: a body in motion will remain in motion unless acted upon by an outside force..
The Nature of Illness may be obtained from the following sources:The Nature of Illness may be obtained from the following sources: 1- The Patient1- The Patient 2- Family Members or Bystanders2- Family Members or Bystanders 3- The Scene3- The Scene.
Scene Size Up Determine the number of patients and the adequacy of resourcesDetermine the number of patients and the adequacy of resources Call for assistanceCall for assistance Other EMS UnitsOther EMS Units Law EnforcementLaw Enforcement Fire DepartmentFire Department HazMatHazMat Negotiating TeamNegotiating Team etc.etc.
The Initial Assessment PurposePurpose To rapidly identify & correct life threatsTo rapidly identify & correct life threats To identify those patients who need rapid evacuationTo identify those patients who need rapid evacuation Minimum Time on scene - Maximum Care En RouteMinimum Time on scene - Maximum Care En Route
Are there any immediate life threats Are there any immediate life threats. Chief ComplaintChief Complaint The reason EMS was called, usually in the patients own words.The reason EMS was called, usually in the patients own words..
The Initial Assessment Mental Status (LevelMental Status (Level of Consciousness)of Consciousness) A - AlertA - Alert V - VerbalV - Verbal P - PainfulP - Painful U - UnresponsiveU - Unresponsive
Bare chest.Bare chest. C irculation Pulse (Rapid/Slow : Weak/Bounding)Pulse (Rapid/Slow : Weak/Bounding) Skin ColorSkin Color TempTemp Major BleedingMajor Bleeding.
VS. Further On-Scene Assessment and Care (Stay-&-Play)Further On-Scene Assessment and Care (Stay-&-Play).
Evaluate Chief ComplaintEvaluate Chief Complaint What circumstances surround this incident What circumstances surround this incident. Is the Mechanism of Injury a high risk for injury Is the Mechanism of Injury a high risk for injury. Conduct Physical ExamConduct Physical Exam Obtain Baseline Vital SignsObtain Baseline Vital Signs.
Yes/NoSignificant MOI. Yes/No Is patient unresponsive or disoriented Is patient unresponsive or disoriented. Can they participate in examination Can they participate in examination. Is the patient under the influence of drugs or alcohol Is the patient under the influence of drugs or alcohol. Can they participate in examination Can they participate in examination .
Trauma Assessment In Patients with NO significant mechanism of injury… Reconsider the Mechanism of InjuryReconsider the Mechanism of Injury Determine Chief ComplaintDetermine Chief Complaint SAMPLE HistorySAMPLE History Baseline VitalsBaseline Vitals Focused AssessmentFocused Assessment
Trauma Assessment Patients without significant MOI Focused Physical ExamFocused Physical Exam –DCAP-BTLS D - DeformitiesD - Deformities C - ContusionsC - Contusions A - AbrasionsA - Abrasions P - Punctures/PenetrationsP - Punctures/Penetrations B - BurnsB - Burns T - TendernessT - Tenderness L - LacerationsL - Lacerations S - SwellingS - Swelling
Consider requesting advanced life support.Consider requesting advanced life support. Reconsider the transport decision.Reconsider the transport decision. Reassess mental status.Reassess mental status. Perform Rapid TraumaPerform Rapid Trauma Baseline VitalsBaseline Vitals SAMPLE HistorySAMPLE History.
Trauma Assessment Patients with significant MOI … RAPID TRAUMA ASSESSMENTRAPID TRAUMA ASSESSMENT –Head-to-Toe Physical Exam –Palpation –Auscultation –Other Senses
Trauma Assessment Patients with significant MOI RAPID TRAUMA ASSESSMENTRAPID TRAUMA ASSESSMENT –DCAP-BTLS D - DeformitiesD - Deformities C - ContusionsC - Contusions A - AbrasionsA - Abrasions P - Punctures/PenetrationsP - Punctures/Penetrations B - BurnsB - Burns T - TendernessT - Tenderness L - LacerationsL - Lacerations S - SwellingS - Swelling
Trauma Assessment Baseline Vital SignsBaseline Vital Signs More than one setMore than one set Look for trending Look for trending HistoryHistory S-A-M-P-L-E S-A-M-P-L-E
Yes/No AVPUAVPU A - Alert V - Verbal P - Painful U -Unresponsive.
Medical Assessment The Responsive Patient… Assess Chief Complaint Assess Chief Complaint Signs & SymptomsSigns & Symptoms O - Onset P – Provokes Q - Quality R - Region/Radiation S - Severity T - Time
Medical Assessment The Responsive Patient… SAMPLE HistorySAMPLE History Focused Medical AssessmentFocused Medical Assessment Baseline Vital SignsBaseline Vital Signs Transport DecisionTransport Decision Detailed Physical ExamDetailed Physical Exam Ongoing AssessmentOngoing Assessment
Medical Assessment The Unresponsive Patient… Rapid Physical AssessmentRapid Physical Assessment Baseline Vital SignsBaseline Vital Signs SAMPLE HistorySAMPLE History Family, co-workers, bystandersFamily, co-workers, bystanders TransportTransport Ongoing assessmentOngoing assessment
More detailed Head-to-Toe examinationMore detailed Head-to-Toe examination Time sensitiveTime sensitive Usually performed en-routeUsually performed en-route Required for any unresponsive patientRequired for any unresponsive patient Required for any multi-trauma patientRequired for any multi-trauma patient Required for any Patient with significant mechanism of injuryRequired for any Patient with significant mechanism of injury –If the mechanism of injury could have caused serious injuries, you must actively assess for additional injuries
Purpose -Purpose - –Determine if there are any changes in the patient’s condition –Identify any missed injuries or conditions –Assess the effectiveness of treatment given and adjust if necessary Performed on both the trauma or medical patientPerformed on both the trauma or medical patient ProcedureProcedure –Repeat Initial Assessment –Reassess Vital Signs –Repeat Focused Assessment –Check Interventions

Full article: Comparison of Four Methods of Paramedic Continuing Education in the Management of Pediatric Emergencies

EMR to EMT Module 2: Patient Assessment – Great Brook Academy

First Aid - Safety Training PowerPoint Presentations

PHTLS - Refresher - OMI

EMS Training, Emergency Medical Responder

EMT 1-1: Introduction to Emergency Care
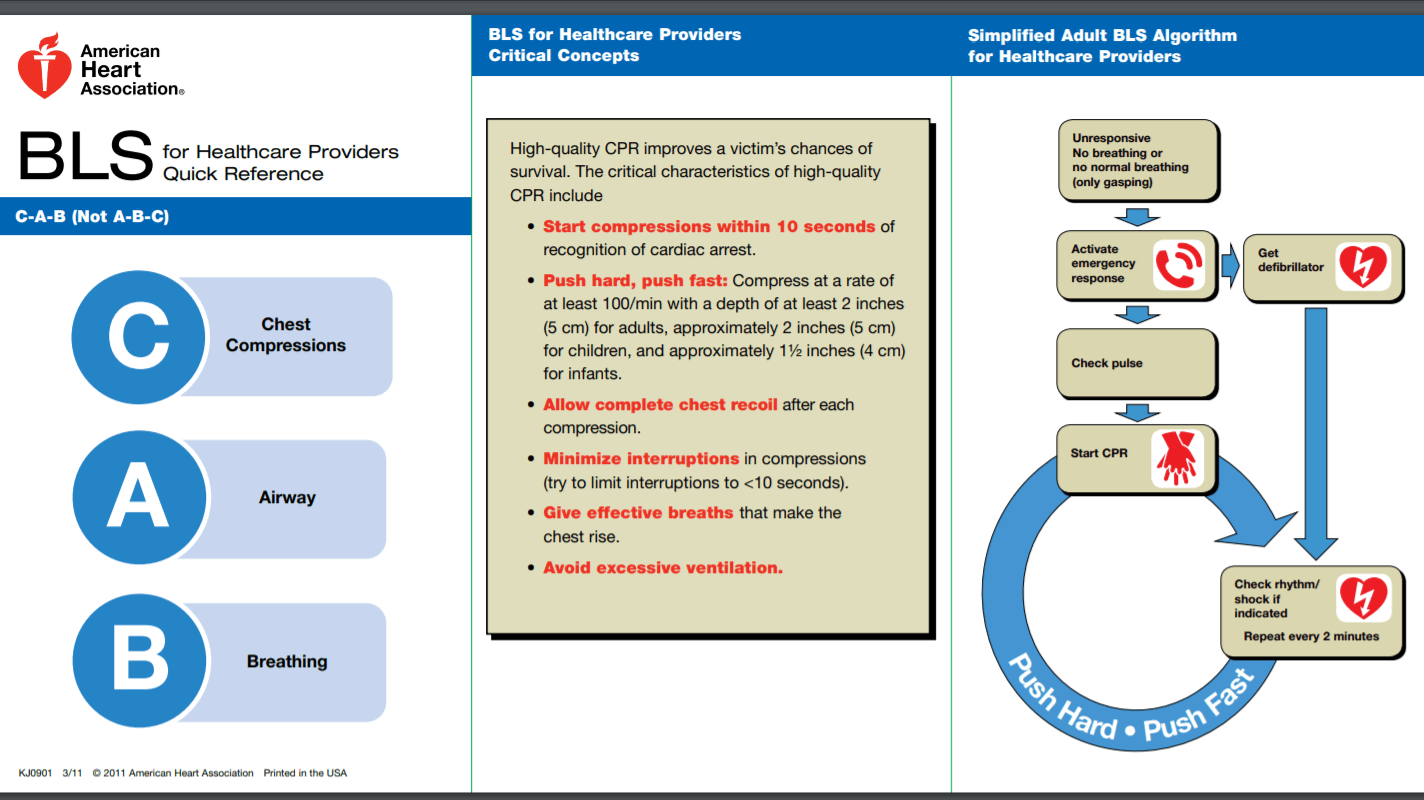
Online CPR Cheat Sheet

The Impact of a Mobile Phone Application for Retention of Bleeding Control Skills - ScienceDirect

BLS CPR - Orange County, Southern California, Fresno, Central Valley

Patient assessment flow chart Emt study, Emt basic, Emergency medical responder

Resuscitation, Free online EMT/Paramedic Refresher Course Refresh 2021 (30 National Hours for NREMT NCCP Program) launches December 15