By A Mystery Man Writer
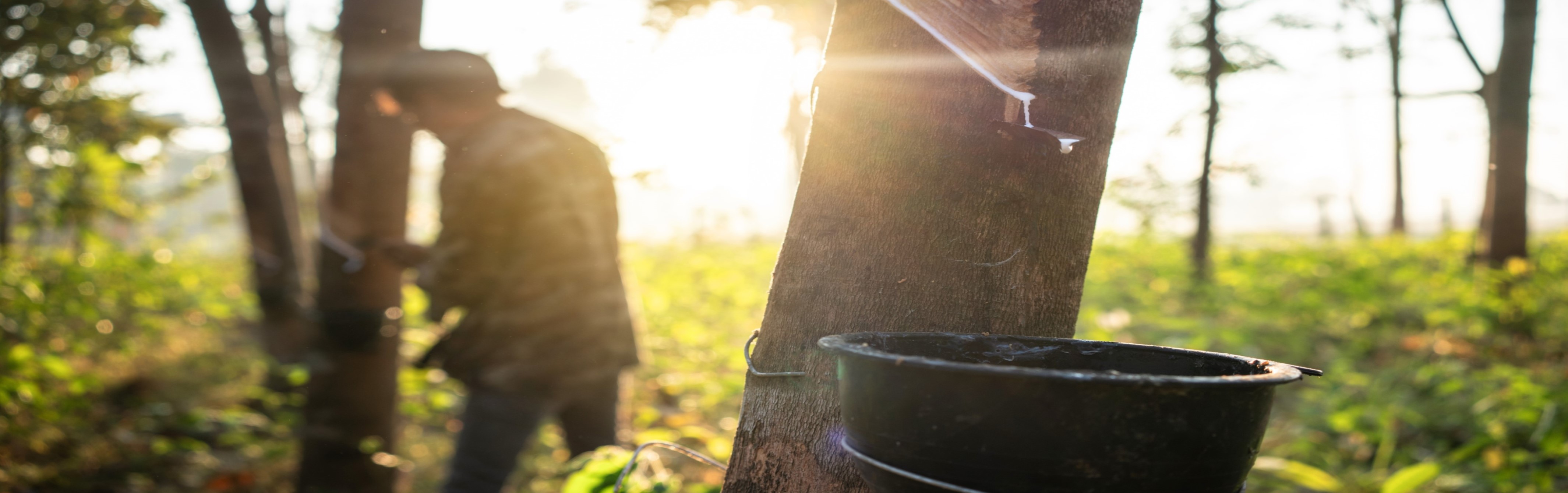

In 1963 Karl Ziegler and Giulio Natta shared the Nobel Prize in Chemistry for the development, in the 1950’s, of their eponymous catalysts for the production of stereoregular polymers from propylene. Their catalyst, an organoaluminum compound coupled with a transition metal, led to the development of synthetic rubbers with a structure closely resembling natural rubber.

Are you ready for a revolution in diving technology? Something BIG

Molecular Structure of Natural Rubber and Its Characteristics

Halcyon Agri Ranked in the Top 3 Most Transparent Rubber

New insight into structure-property relationships of natural

Molecular Structure of Natural Rubber and Its Characteristics
10.4: Rubber and Other Elastomers - Chemistry LibreTexts

4.8: Natural and Synthetic Rubbers - Chemistry LibreTexts
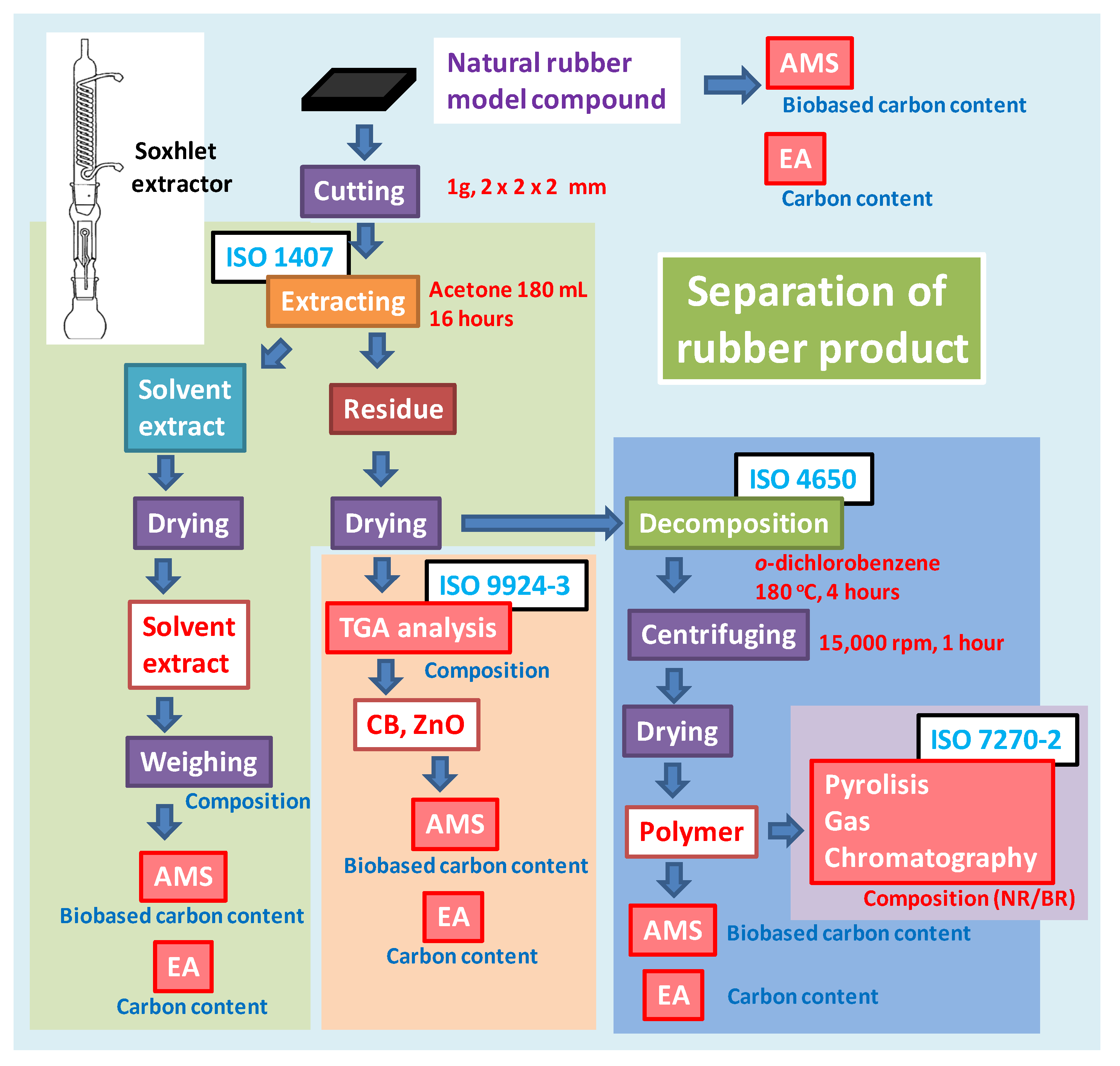
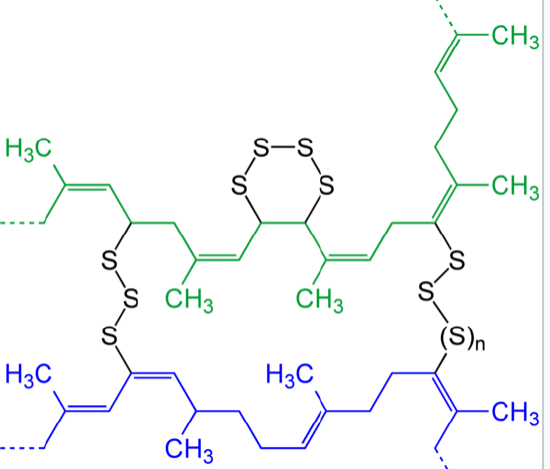
Polymers, Free Full-Text

Molecular Structure of Natural Rubber and Its Characteristics
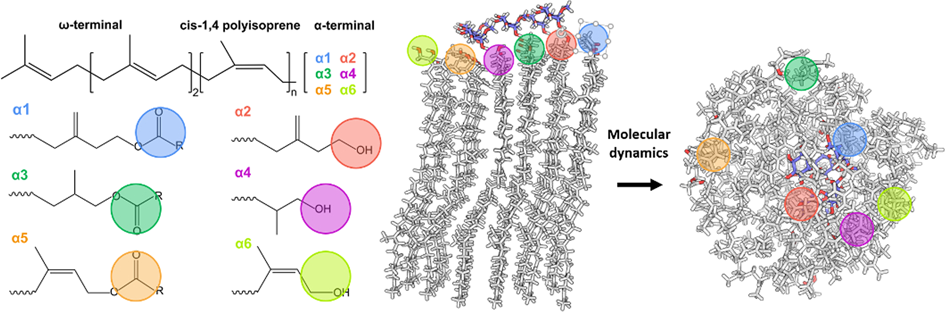
Computational study of the interaction between natural rubber α